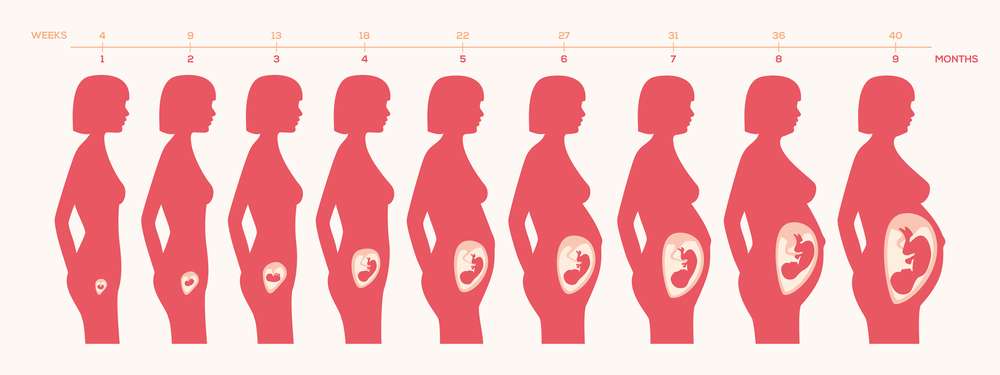
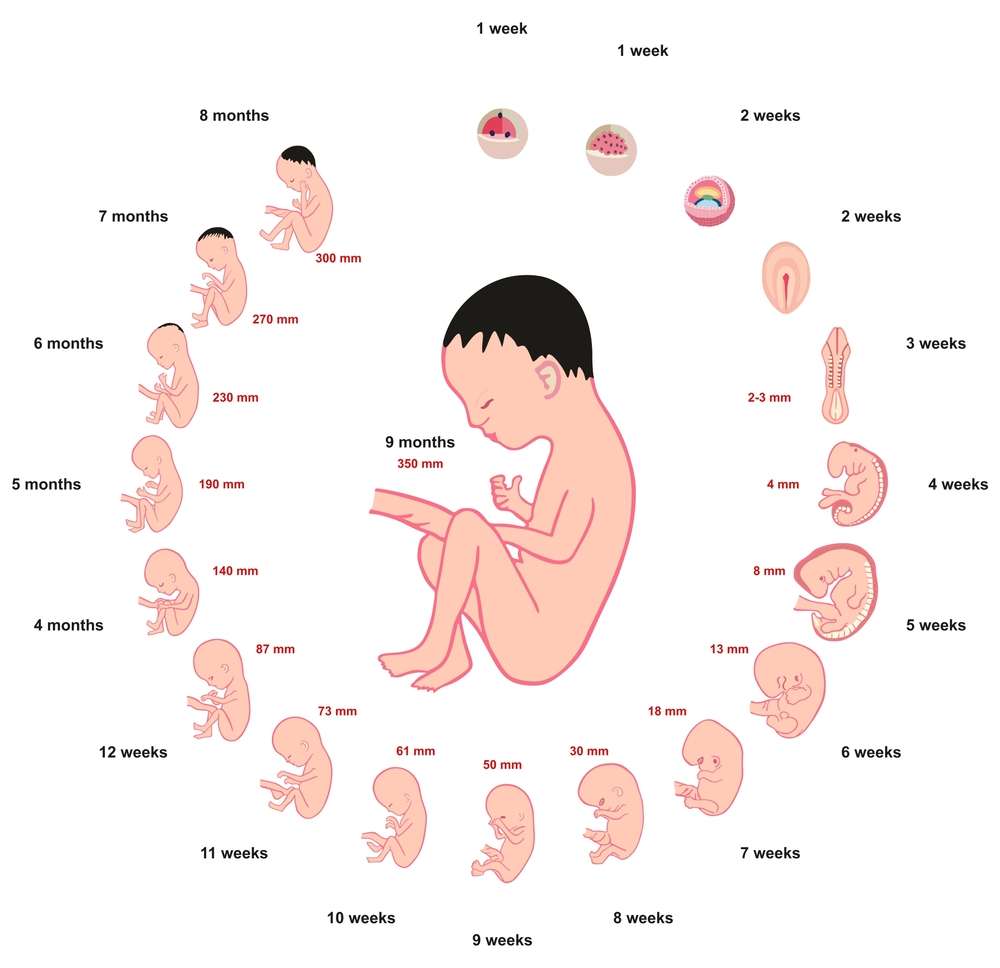
Pregnancy week by week
Pregnancy Week By Week:
Pregnancy is a beautiful journey that brings joy and anticipation for the arrival of a precious little one. The entire process is filled with countless changes and developments, both for the mother and the growing baby. In this comprehensive guide, we will take you through each week of pregnancy, exploring the unique milestones and transformations that occur along the way. Get ready to embark on this incredible adventure, Pregnancy week by week.
Pregnancy 1 Weeks:
- The adventure begins: Week 1 symbolizes the beginning of pregnancy, even if conception has not yet occurred.
- The monthly menstrual cycle: During this week, a woman’s body loses the uterine lining in preparation for a possible pregnancy.
- Fertilization: If fertilization occurs, the egg will come into contact with the sperm within 24 hours, kicking off the process of producing a new life.
Pregnancy 2 Weeks:
- The fertilized egg attaches itself into the uterine wall, signifying the start of the pregnancy.
- Early development: A collection of cells called a blastocyst begins to split and divides to become the placenta and the embryo.
- Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), the pregnancy hormone, may begin to rise, causing a variety of physical and emotional changes.
Pregnancy 3 Weeks:
- Rapid cell division: As the embryo develops the central nervous system, heart, and digestive system, it continues to divide at a rapid rate.
- Amenorrhea: The absence of menstruation is sometimes one of the first indicators of a possible pregnancy.
- Home pregnancy tests may begin to produce positive results, confirming the presence of hCG in the body.
Pregnancy 4 Weeks:
- Pregnancy confirmation: During this week, medical confirmation is typically sought to confirm the pregnancy and estimate the delivery date.
- Major organ formation: Major organs such as the brain, spinal cord, and heart begin to form in the embryo.
- Hormonal changes: Elevated levels of progesterone and estrogen might cause symptoms such as breast soreness and nausea.
Pregnancy 5 weeks:
- Primitive placenta: The placenta begins to develop and plays an important role in supplying nutrition and oxygen to the developing embryo.
- Missed menstruation: Most women will have missed their period by week 5, confirming the pregnancy.
- Breast changes: Breasts may grow more sensitive and slightly bigger as they prepare for milk production later in pregnancy.
Pregnancy 6 weeks:
- Heartbeat detection: An ultrasound or a Doppler equipment can detect the baby’s heartbeat.
- Formation of the neural tube: The neural tube, which will eventually develop into the baby’s brain and spinal cord, begins to take shape.
- Morning sickness: Nausea and vomiting, also known as morning sickness, may begin to plague some pregnant women.
Pregnancy 7 Weeks:
- Emergence of facial characteristics: The baby’s face features, including as eyes, ears, and a small mouth, become increasingly distinct.
- Bloating and weight gain: Due to increased blood volume and hormonal oscillations, rapid changes in the body cause bloating and potential weight gain.
- Increased sense of smell: Many pregnant women experience an increase in their sense of scent, which may be both delightful and overwhelming.
Pregnancy 8 Week:
- Limb development: The baby’s limbs and fingers start to form, taking on a small but distinct shape.
- strange food desires and aversions: As taste receptors change, many expectant mothers have strange food cravings and aversions.
- Fatigue and mood swings: This week’s increased progesterone levels may contribute to fatigue and mood changes.
Pregnancy 9 Weeks:
- Rapid brain development: The baby’s brain grows rapidly, with new neurons developing at an astounding rate.
- Morning sickness persists: Nausea and vomiting may continue to be a part of many pregnant women’s daily lives.
- Urination is more frequent as the uterus develops, putting strain on the bladder and necessitating more frequent trips to the lavatory.
Pregnancy 10 weeks:
- Fingernails and toes: The baby’s fingernails and toes begin to form, like small translucent crescents.
- Emotional rollercoaster: Hormonal changes can cause heightened emotions and mood swings.
- Skin changes: Pregnant women may have skin changes such as hyperpigmentation or the formation of stretch marks.
Pregnancy 11 Weeks:
- Reflexes and motions: Although the baby’s limbs are still too little to be felt by the mother, they can produce jerky movements.
- Increased hunger: As the baby’s nutritional requirements expand, many pregnant women may notice an increase in appetite.
- Congestion and nosebleeds: Hormonal fluctuations can cause nasal passage enlargement, resulting in congestion and rare nosebleeds.
Pregnancy 12 Weeks:
- The first trimester, which is frequently accompanied by persistent early pregnancy symptoms, will come to a conclusion by the end of week 12.
- Skeletal development: The bones of the baby begin to develop and stiffen, preparing them for future growth and mobility.
- Reduced fatigue and nausea: As the first trimester comes to an end, many women report a reduction in exhaustion and morning sickness.
Pregnancy 13 weeks:
- Baby’s sex: Certain prenatal procedures, such as non-invasive prenatal testing (NIPT) or ultrasound, may be able to reveal the sex of the baby to some expectant parents.
- Teeth development: The baby’s tooth buds begin to grow beneath the gums, laying the groundwork for tooth development after delivery.
- Increased energy: As the placenta takes over hormone synthesis, many women regain energy and begin to feel more like themselves.
Pregnancy 14 weeks:
- Changes visible: The baby’s body proportions improve, with longer limbs and a more defined neck.
- Heartburn and indigestion: Hormonal shifts can relax the muscles that typically keep stomach acid at bay, resulting in heartburn and indigestion.
- Increased blood flow and hormone levels during pregnancy can give the skin a beautiful and healthy glow.
Pregnancy 15 weeks:
- Hearing development: The inner ear structures of the newborn develop, allowing them to hear sounds from the outside world, including the mother’s speech.
- Round ligament pain: As the uterus develops, the round ligaments that support it may stretch, causing discomfort or acute sensations.
- Increased vaginal discharge: During pregnancy, the body creates extra mucus to protect the reproductive organs and prevent infections.
Pregnancy 16 weeks:
- Quickening: During this week, many expectant moms feel the first flutters of the baby’s movements, known as quickening.
- Hair growth: The baby’s scalp begins to produce small hair strands, laying the groundwork for their future hairstyle.
- Skin darkening: Some pregnant women may have skin darkening, sometimes known as chloasma or the “mask of pregnancy,” as a result of increased pigment production.
Pregnancy 17 Weeks:
- Audible heartbeat: During a prenatal checkup, a healthcare provider may be able to hear the baby’s heartbeat using a stethoscope.
- Weighing in: As fat stores expand and muscular mass grows, the baby’s weight begins to rise considerably.
- Varicose veins: As the body’s blood volume increases, veins, particularly those in the legs, can become bloated and noticeable.
Pregnancy 18 Weeks:
- Baby movement detection: Many moms can now detect their babies’ motions, known as “flutter kicks,” more clearly.
- Footprints and fingerprints: As ridges and lines appear on the baby’s small fingers and toes, their distinctive footprints and fingerprints begin to form.
- Hormonal fluctuations can cause nasal passages to expand, resulting in congestion and difficulties breathing through the nose.
Pregnancy 19 Weeks:
- Vernix caseosa: The vernix caseosa protective layer begins to cover the baby’s skin, sheltering it from the amniotic fluid.
- Dreaming begins with: During this week, the baby begins to experience rapid eye movement (REM) sleep, which is connected with dreaming.
- Leg cramps: For some pregnant women, changes in blood circulation and increased pressure on the legs might cause periodic leg cramps.
Pregnancy 20 weeks:
- By week 20, the pregnancy has reached its midway point, and the baby’s growth is increasingly noticeable to the outside world.
- Hearing amniotic noises: The infant is now able to hear sounds from outside the womb, such as the mother’s heartbeat or music.
- Edema: Swelling, particularly in the feet and ankles, may become more evident during this stage of pregnancy due to water retention.
Pregnancy 21 Weeks:
- Eyebrows and eyelashes: As the newborn grows, his or her brows and eyelashes begin to grow, framing the developing eyes.
- Darkened nipples: In preparation for breastfeeding, the body’s increased production of melanin might cause the nipples to darken.
- Difficulty sleeping: As the baby grows and presses against the mother’s internal organs, finding a comfortable resting posture may become difficult.
Pregnancy 22 Weeks:
- Rapid brain development: The baby’s brain develops at an incredible rate, with millions of neurons being generated every day.
- Hiccups: The baby may get hiccups, which are rhythmic movements in the womb.
- Backaches: As the baby’s weight grows, the mother may experience lower back pain and discomfort.
Pregnancy 23 Weeks
- The baby’s voice begins to develop, creating the groundwork for their initial cries following birth.
- Braxton Hicks contractions: The mother may occasionally begin to experience Braxton Hicks contractions, which are moderate and irregular uterine contractions.
- Breathing difficulties: As the uterus grows, it puts pressure on the diaphragm and lungs, causing sensations of breathlessness or increased effort to breathe.
Pregnancy 24 Weeks:
- Rapid eye movement (REM) sleep: Similar to adults, the baby’s eyes will now travel back and forth rapidly during REM sleep.
- Gestational diabetes screening: Your healthcare practitioner may prescribe a glucose screening to check for gestational diabetes around this time.
- Swollen ankles and feet: Edema, or swelling, in the lower extremities may worsen, necessitating the use of suitable footwear and regular leg elevation.
Pregnancy 25 Weeks:
- Surfactant production: Following delivery, the baby’s lungs begin to create surfactant, a chemical that keeps the air sacs from collapsing and aids in breathing.
- Colostrum production: The mother’s breasts may begin to produce colostrum, a nutrient-rich pre-milk fluid that feeds the baby in the days following birth.
- Lightheadedness: Hormonal fluctuations might induce a reduction in blood pressure, resulting in lightheadedness or dizziness on occasion.
Pregnancy 26 Weeks:
- Intense brain activity: As the newborn begins to recognize voices and sounds from the outside world, his or her brain activity becomes increasingly sophisticated.
- Kicks and jabs: The baby’s movements get stronger and more frequent, and they may react to external stimuli like bright lights or loud noises.
- Increased vaginal discharge: A protective substance known as leukorrhea may be more visible, aiding in the prevention of vaginal infections.
Pregnancy 27 Weeks:
- Lung development: The baby’s lungs continue to mature, with air sacs producing a chemical known as surfactant.
- Sleep and wake cycles: The baby develops consistent sleep and wakefulness patterns, which the mother may begin to observe.
- Pelvic discomfort: The increasing uterus’s pressure can produce pelvic pain or hurting, particularly around the pubic bone.
Pregnancy 28 Weeks:
- Third trimester: With week 28, the pregnancy officially enters the third trimester, signaling the end of the road to delivery.
- Fetal movements: The baby’s kicks, punches, and stretches grow more noticeable and may even be seen from outside the womb.
- Heartburn and indigestion: As the uterus grows, it can push against the stomach, causing heartburn and indigestion.
Pregnancy 29 Weeks:
- Sensory development: As the infant responds to diverse stimuli in the womb, his or her senses, including taste, touch, and hearing, grow more developed.
- Increased fat stores: The baby’s fat stores continue to build, providing insulation and energy reserves for future growth.
- Swelling and discomfort: During this time, edema and general discomfort in the hands, feet, and joints may become more pronounced.
Pregnancy 30 Weeks:
- Braxton Hicks contractions: As the mother’s body prepares for labor, she may experience more frequent and visible Braxton Hicks contractions.
- Position of the baby: By week 30, the baby may have settled into a head-down position, preparing for the delivery process.
- Shortness of breath: As the uterus grows, it puts pressure on the diaphragm, making the mother feel more breathless, especially when exercising.
Pregnancy 31 Weeks:
- Growth spurts in the infant: The baby grows significantly during this week, growing both weight and length.
- Fluid retention can induce swelling in the hands and fingers, making rings feel tighter or more painful to wear.
- Difficulty sleeping: Finding a comfortable resting position with an expanding belly can be difficult, resulting in disrupted sleep habits.
Pregnancy 32 weeks:
- Immune system maturation: The baby’s immune system matures further as antibodies from the mother assist protect them against infections after birth.
- Preparing for lactation: The mother’s breasts may begin to generate more colostrum in preparation for breastfeeding.
- Increased pelvic pressure: As the baby grows and settles into the pelvis, the strain on the bladder and pelvic region might become more intense.
Pregnancy 33 Weeks:
- Brain-cell renewal: As the baby’s brain develops, brain cells proliferate and build more intricate connections.
- Light sensitivity: The baby’s eyelids can now detect light, prompting them to open or close their eyes in reaction to bright light outside the womb.
- Varicose veins: Increasing weight and pressure can aggravate or possibly cause varicose veins, producing discomfort and visible veins.
Pregnancy 34 Weeks:
- Final positions: Most infants will be in a head-down position by week 34, however others may still be breech or transverse.
- Nesting instinct: During pregnancy, many women experience a burst of energy and an intense need to prepare for the baby’s arrival, which is known as the “nesting instinct.”
- Heartburn and indigestion: As the uterus grows, it can press on the stomach, causing heartburn and indigestion, especially after meals.
Pregnancy 35 Weeks:
- Immune system boost for the infant: During the first few months of life, the baby benefits from the mother’s antibodies, which strengthen their own immune system.
- Frequent urination: Even if the bladder isn’t totally full, the strain on it can induce more trips to the lavatory.
- Lower back pain: As the baby’s head settles into the pelvis, pressure on the lower back increases, causing discomfort or mild pain.
Pregnancy 36 Weeks:
- Positioning for birth: By now, most babies will have taken a head-down position, preparing for their passage down the birth canal.
- Braxton Hicks contractions become very intense: The irregular contractions might become more prominent, and some of them might even mimic true labor contractions.
- Swollen feet and ankles: Edema can cause puffy and swollen feet and ankles, necessitating elevation and support.
Pregnancy 37 Weeks:
- final preparations: The pregnancy is deemed full-term at week 37, allowing the baby to be delivered safely at any time.
- Lightening: The baby’s head begins to descend towards the pelvis, causing the mother’s form to shift and making breathing easier.
- Nesting frenzy: As the desire to prepare for the baby’s arrival grows stronger, many pregnant women indulge in obsessive cleaning and arranging activities.
Conclusion:
The journey of pregnancy week by week is a wonderful experience full of wonder and amazement. As the baby grows and develops, each week brings new surprises, difficulties, and milestones. Expectant mothers and their loved ones can better appreciate the remarkable journey leading to the birth of a precious new life if they understand the changes that occur over the weeks. Stay tuned for the next chapter of our “Pregnancy Week by Week” series, in which we will continue to investigate the incredible alterations taking place within the pregnant mother’s body and the wonderful baby growing within.


Lovely