Anterior Placenta
When the placenta develops in front of the uterine wall, it is called an anterior placenta. Pregnancy is frequent for this illness, which can make it more difficult for you to feel your baby kick or for a medical professional to locate the baby’s heartbeat. Usually, it doesn’t lead to any difficulties.
What is an Anterior Placenta?
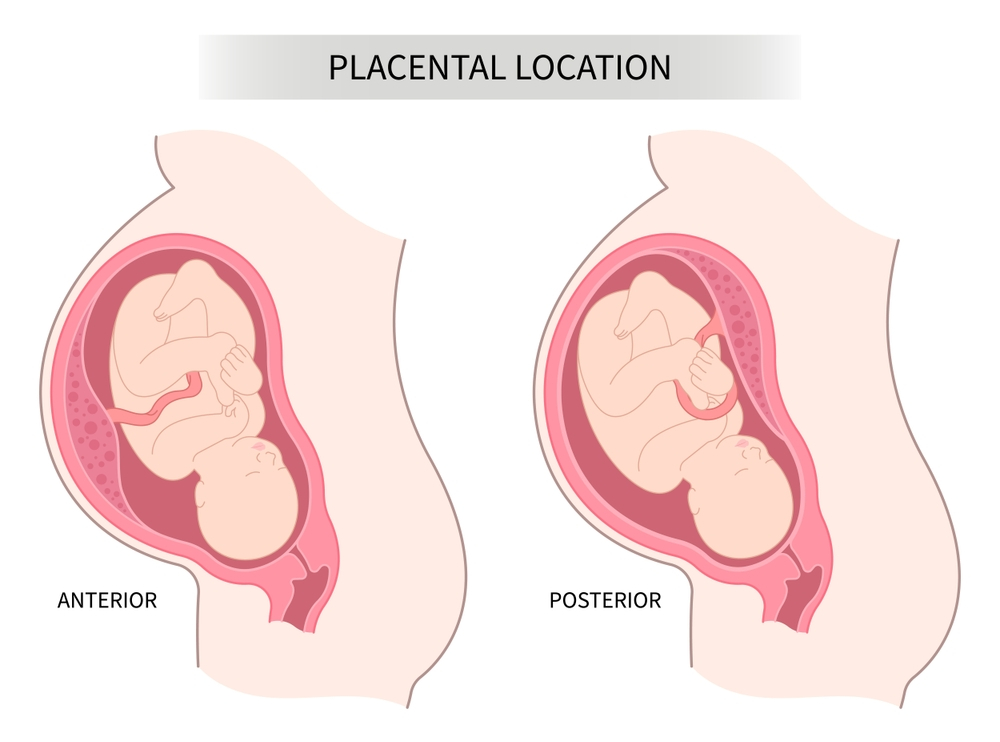
When the placenta is anterior, it is situated in the front of the uterus, closest to the belly. It is run of the mill during pregnancy and commonly not justification for caution. About 18 to 21 weeks into the pregnancy, an ultrasound is used to make the diagnosis.
Where a treated egg inserts in your uterine wall is where your placenta structures. Through the umbilical cord, oxygen, hormones, and nutrition are transferred from you to your child. It also helps your infant get rid of trash.
An anterior placenta develops at the front of the uterus instead of the typical location of the placenta, which is on top or the back of the uterus. A front placenta may be contrasted with a pad between your stomach and your unborn kid.
The placenta can migrate as your uterus expands, meaning that as your pregnancy goes on, it may begin in the front and move toward the top. You or your kid experience no medical problems because of a front placenta. Most of the time, an anterior placenta has no noticeable impact.
Benefits of Anterior Placenta
- The anterior placenta, which is situated at the front of the uterus, has the ability to act as a cushion between the mother’s abdominal wall and the baby’s movements. As a result, there may be fewer painful or painful kicks overall, which is especially beneficial as the pregnancy goes on and the baby gets bigger.
- Some women may feel less discomfort or fewer abrupt movements as a result of the cushioning effect, which can be especially helpful as the pregnancy progresses.
- Decreased Risk to Mother and Baby: An anterior placenta is not inherently more dangerous for the mother or the child; rather, it is thought of as a typical variation. It is noteworthy that although it may impact the mother’s perception of sensations during childbirth, difficulties usually do not arise.
- The placenta acts as a barrier to protect the baby from harm, no matter where it is located. An anterior placenta gives the developing fetus an extra layer of protection because it is positioned at the front of the uterus.
- For many women, an anterior placenta is just a typical placental variation; it doesn’t always mean that there are any problems. It’s just one of the many distinctive features that add individuality to every pregnancy.
- Some women discover that having the anterior placenta in place may make their daily routines more comfortable because they may experience fewer abrupt movements, which can occasionally be upsetting or uncomfortable.
Symptoms of Anterior placenta
More often than not, having a front placenta isn’t unsettling and doesn’t bring about numerous side effects. Observable symptoms of an anterior placenta include:
- Baby’s heart rate: Using a Doppler ultrasound, it might take the doctor longer to find the baby’s heartbeat. To find the heart rate of your unborn child, the doppler is moved across your abdomen. Because your baby and the Doppler are separated by the placenta, it may take longer.
- Baby’s movement: If your placenta is posterior, you might feel punches or kicks later than others. The majority of pregnant women experience kicks around week eighteen, but those who have anterior placentas might not experience kicks until week twenty. Additionally, because the placenta is separating your baby from your belly, they may feel softer or weaker.
Causes of Anterior Placenta
Nothing under your control can result in an anterior placenta. An egg will implant on the uterine walls after it has been fertilized. Your placenta will grow in this area. The uterus’s ability to function normally and the way your pregnancy is handled are unaffected by the placenta growing in front of it.
Does having an anterior placenta carry any risks?
An anterior placenta is associated with certain risks. The majority of the risks don’t endanger you or your child:
- Placenta previa:This happens when the cervix is wholly or partially encased by the placenta. It can lead to complications and moderate to severe vaginal bleeding.
- C-section: Because placenta previa prevents your baby from leaving your vagina, you are more likely to have a cesarean delivery (c-section).
- Back labor: The odds of your baby being in the OP position (occiput posterior) are higher if you have an anterior placenta. This indicates that your baby’s face is up and their head is down because their back is against your back. This may result in a longer labor and increased back pain.

Why does the placenta erupt anteriorly in some people?
The explanation a treated egg inserts toward the front of the uterus rather than elsewhere in the uterus is obscure. The placenta develops and an egg implant normally against the front wall of the uterus. It has no effect on the placenta’s capacity to sustain your kid through nutrition.
How Common is anterior placenta?
A placenta anterior is typical. Up to 50% of pregnancies end with the placenta in front of the uterus. According to one study, individuals with o-positive blood appear to have anterior placentas more frequently. Another study discovered that the fertilized egg implanting on the front of your body after conception can be related to sleeping on your stomach. Both of these investigations require additional scientific proof to be validated.
What effects on pregnancy might an anterior placenta have?
A baby born with an anterior placenta is not harmed in any way. The main effect on your pregnancy is that it may take longer for you to feel the kick of your unborn child. For the same reason, certain fetal tests (like amniocentesis) may be difficult to perform or it may be more difficult to locate your baby’s heartbeat during a Doppler ultrasound.
How is an anterior placenta diagnosed?
Using an ultrasonography, your healthcare provider will locate the placenta. This ultrasound, also known as an anatomy scan, is performed between weeks 18 and 21 of pregnancy. The size of your baby and all of its organs are measured with this ultrasound. An anterior placenta is not diagnosed until about 20 weeks because it is common for the placenta to shift positions as the uterus grows.
Is an anterior placenta treated in any way?
Since an anterior placenta rarely causes complications, there is no treatment for it. Only if you have placenta previa or other pregnancy-related conditions is treatment required.
Can an anterior placenta still be delivered vaginally?
Yes, even with an anterior placenta, vaginal delivery is still possible. It makes no difference to delivery outcome if the placenta is anterior. The only condition that could interfere with a vaginal delivery is placenta previa.
Does a placenta anteriorly impact the outcome of a C-section?
No, an anterior placenta has no bearing on your cesarean section. To determine the ideal location for the incision and to determine the placenta’s position, your healthcare provider will use ultrasound technology.
What does baby movement feel like with anterior placenta?
When the placenta is positioned anteriorly, the experience of feeling fetal movements may differ slightly from other pregnancies in which the placenta is positioned posteriorly. The mother’s abdominal wall and the baby’s movements are cushioned by the anterior placenta, which is situated at the front of the uterus. This can cause the fetal movement sensations to change or be delayed, which can affect how a mother experiences these movements.The infant’s movements could be described by women with an anterior placenta as:
- Subtle Fluttering: In the beginning, there may be fewer noticeable movements, more akin to a flutter or a mild tickling feeling. Compared to what some people might experience in the absence of an anterior placenta, this can be less severe.
- Gentle Rolls or Swooshes: Rather than feeling like sharp or forceful kicks, movements may become more akin to gentle rolling or swooshing as the pregnancy goes on. This is because of the placenta’s cushioning function.
- Delayed Perception: Because of the placenta’s position, mothers may experience a delayed onset of movement or initially have difficulty identifying the baby’s precise movements.
- Less Intense Movements: Compared to pregnancies without an anterior placenta, the movements may not be as strong or obvious. Because the placenta lessens the impact of strong kicks and jabs, some women may not feel them as strongly.
Conclusion
An expectant mother’s pregnancy experience may be impacted by the placenta’s position, particularly if it is anterior. It usually does not hurt the mother or the unborn child, though it can occasionally obstruct ultrasound visibility and cause delayed feelings of fetal movements.
But it’s important for expectant mothers to discuss any worries they may have with their healthcare provider, such as decreased movement or other issues associated with an anterior placenta. Throughout the pregnancy, routine prenatal checkups, monitoring, and additional scans as needed can reassure and guarantee the health of the developing baby and the mother.