Placenta Previa
What is placenta previa?
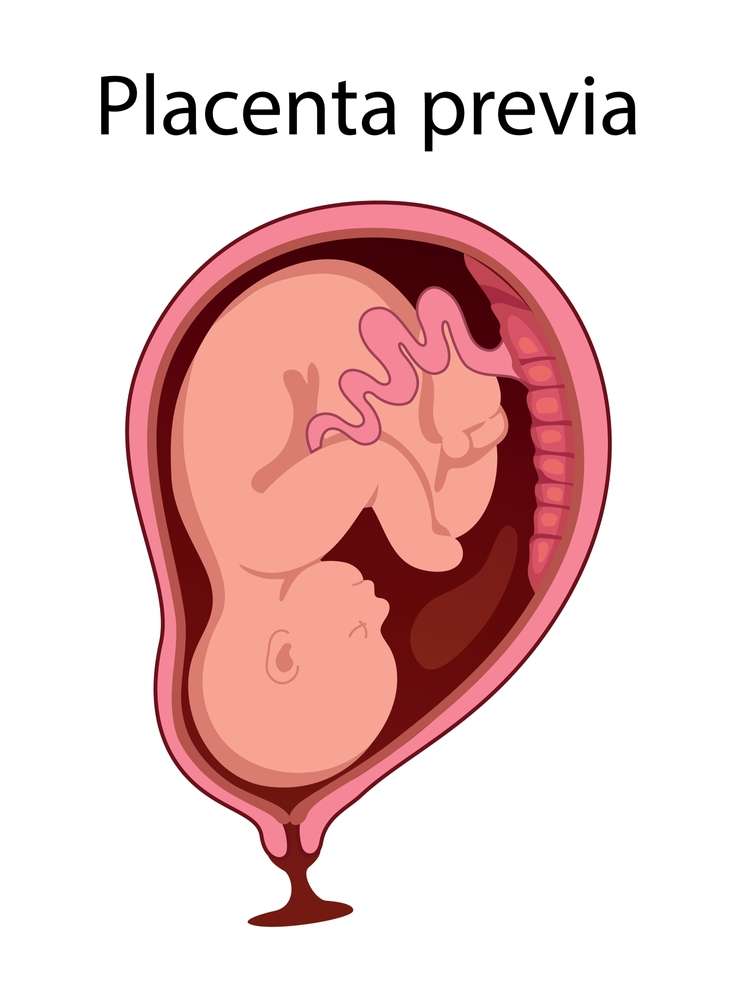
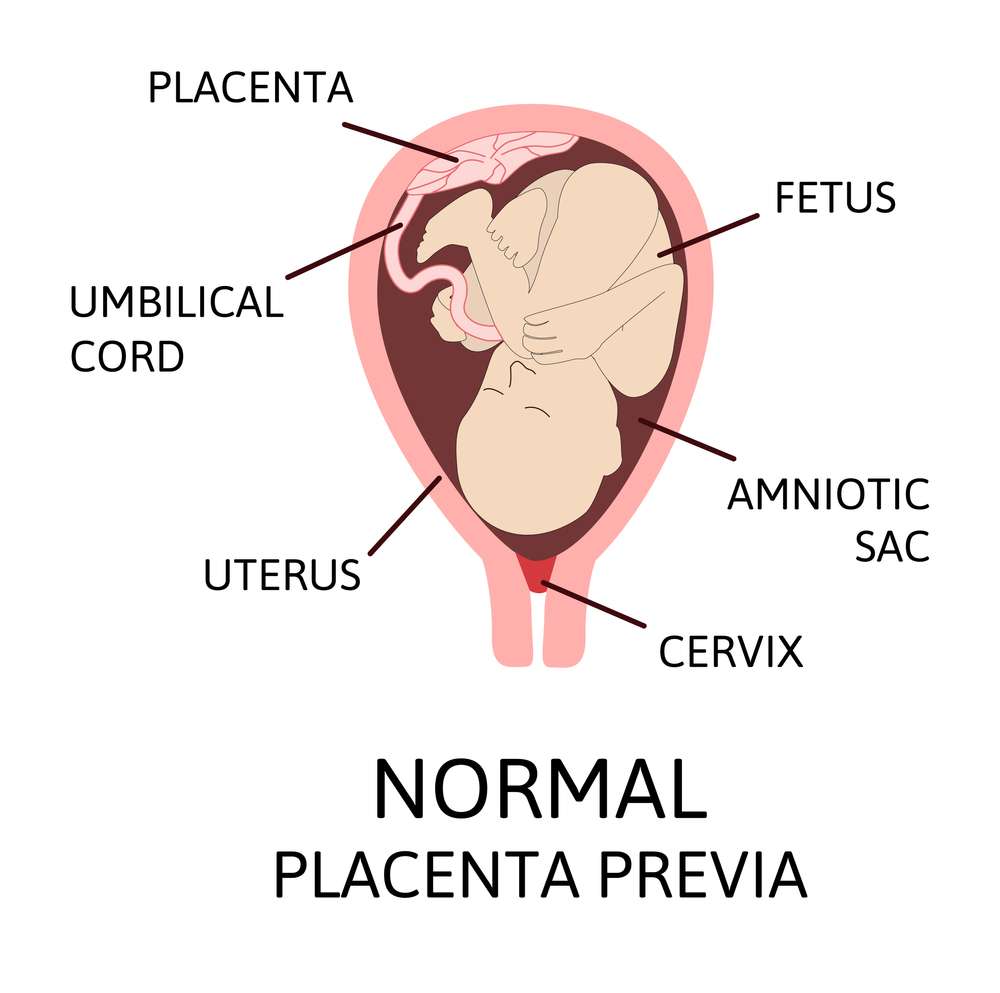
When the placenta entirely or partially covers the uterus’s opening (cervix), it is known as placenta previa.During pregnancy, an organ called the placenta grows inside the uterus.It capabilities to give the infant nourishment and oxygen as well as to eliminate squander.Your child and the placenta are connected by the umbilical harmony.
The placenta is frequently secured to the top or side of the uterus’ inward wall.The placenta attaches lower in the uterus in cases of placenta previa.Subsequently, the cervix is to some extent covered by placental tissue.It may lead to bleeding during labor, during the pregnancy, or after delivery.Pregnancy-related alterations to the uterus and placenta may cause the issue to resolve itself.If it doesn’t, a cesarean section (C-section) is used to deliver the child.
Placenta previa Symptoms
Placenta previa is a pregnancy condition in which the placenta implants in the lower region of the uterus, near or covering the cervix.The placenta is an organ that adheres to the upper section of the uterine wall and supplies oxygen and nourishment to the developing embryo.In the instance of placental previa, however, the placenta partially or completely covers the cervix.There are several types of placenta previa, including:
- Placenta Previa Complete: The placenta entirely covers the cervical opening.
- Partial Placenta Previa: The placenta covers the cervical opening partially.
- Marginal Placenta Previa: The placenta is near the cervix but does not cover it.
Placental previaa can cause a variety of pregnancy issues, including:
- Painless vaginal bleeding, which can be rapid and severe, is one of the most prevalent symptoms.
- This type of bleeding can happen at any time during pregnancy, although it is most prevalent in the third trimester.
- Preterm birth: Placenta previaa raises the likelihood of a baby being born before reaching full term.
- Because vaginal delivery with placental previa can be risky due to the possibility of heavy bleeding, most cases result in a C-section delivery.
- Anemia: Continued draining episodes can bring about maternal pallor, which can adversely affect the mother’s wellbeing.
The precise etiology of placental previa is not always known, although some risk factors, such as:
- C-sections or uterus procedures in the pastMultiple pregnancy (for example, twins or triplets)
- Maternal age (being over the age of 35)
- Pregnancy and smoking
- A previous pregnancy with placenta previa.
- Ultrasound imaging is commonly used to diagnose placenta previa.
Note:
The severity of the problem and the stage of pregnancy influence treatment and management of placenta previa.In some circumstances, enforced bed rest or hospitalization may be advised to monitor bleeding and the mother and baby’s wellbeing.
An emergency C-section may be required if the bleeding becomes serious or life-threatening.Pregnant women with placenta previa must collaborate closely with their healthcare providers to secure the best possible outcome for both the mother and the baby.
In order to manage this illness, regular prenatal care and attentive monitoring are required.
- After 20 weeks of pregnancy, bright crimson vaginal bleeding that usually causes little pain is the primary symptom of placenta previa.
- Spotting can occasionally occur before a situation involving significant blood loss.
- The painful uterine contractions that precede labor may also cause bleeding.
- Other factors that can cause bleeding include intercourse and being examined by a doctor.
- Bleeding may not start until labor for some women.
- Often, bleeding occurs for unclear reasons.
Risk Factors:
- Women who have had a previous C-section or who have had a baby are more likely to have placental previa.
- Have scars from prior medical procedures or techniques on the uterus
- Had a previous pregnancy with placenta previa.
- After undergoing a surgery using assisted reproductive technology (ART) to address infertility, are pregnant.
- Are 35 years of age or older and carrying more than one fetus.
- cocaine complications from smoking
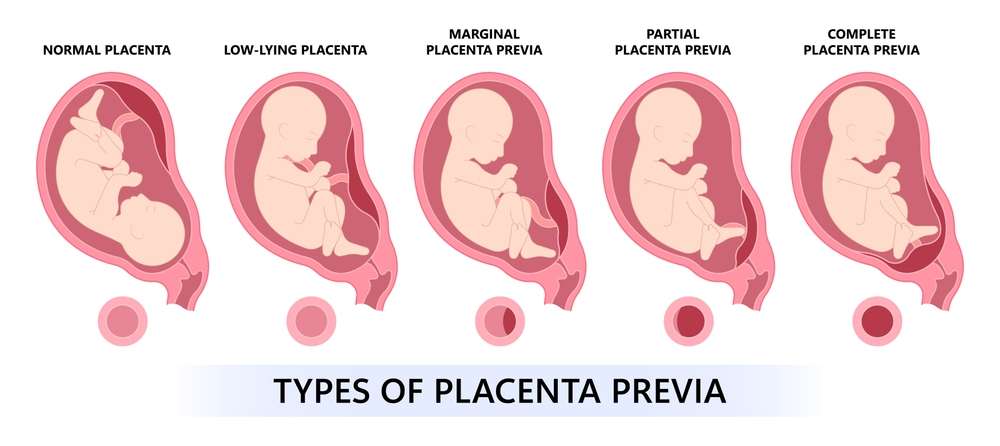
Placenta previa types:
Complete placenta:
The placenta thoroughly covers the cervical opening in this case.The placenta totally impedes the cervical opening, making vaginal conveyance impossible.For instances of full placenta previa, a cesarean segment (C-area) is normally the suggested method of birth.
Partial placenta:
The placenta somewhat covers yet doesn’t totally limit the cervix in fractional placenta previa.This means that the child can go through some space during birthing, yet it is as yet a high-risk circumstance.The decision between vaginal conveyance and C still up in the air by the degree of inclusion and different models.
Marginal placenta:
This condition happens when the placenta’s edge comes to or is very near the cervical opening however doesn’t cover it.This sort of placenta previa is less extreme than complete or fractional previa, and it could be related with a lower chance of pregnancy and work drain issues.Vaginal conveyance might be conceivable in certain examples, yet it should be painstakingly checked.
Low-lying placenta:
Some women might have a placenta that is near however doesn’t totally cover the cervix.This issue is all the more ordinarily known as a low-lying placenta than genuine placenta previa.In most instances of a low-lying placenta, the placenta will normally move away from the cervix as the uterus extends during pregnancy, fixing the issue without consequences.Ultrasounds are used consistently to screen the placental position.
Complications
In order to lower the chance of these severe issues, your healthcare practitioner will monitor both you and your unborn child if you have placenta previa:
- Bleeding:It is possible for there to be severe vaginal bleeding (hemorrhage), which could be life-threatening, during pregnancy, labor, delivery, or in the first few hours following birth.
- preterm delivery:An emergency C-section may be necessary before your baby reaches term if there is severe bleeding.
- Spectrum of placental accretion:The placenta accreta spectrum is a collection of disorders that include placenta previa.
- The placenta grows into or through the uterine wall under these circumstances.
- The risk of placenta accreta bleeding during pregnancy or during and after delivery is very high.
Placenta previa treatments:
The type and degree of placenta previa, the stage of pregnancy, and the presence of any problems all influence treatment and management of placenta previa. Here are some common methods for dealing with placenta previa:
- If placenta previa is found early in pregnancy and there is no active bleeding, the healthcare professional may advise close monitoring. This includes regular check-ups and ultrasounds to track the position of the placenta and examine the health of the mother and baby.
- Women with placenta previa may be recommended to refrain from engaging in activities that may cause bleeding or uterine contractions. This frequently includes pelvic rest, which means no sexual intercourse and no intense exercise.
- Hospitalization may be required in cases of substantial bleeding or other problems. This enables healthcare providers to closely monitor the mother and infant, give essential medical measures, and be prepared in the event of an emergency.
- In the event that a women has broad draining and becomes weak, she might require blood bondings to supplant lost blood and lift her hemoglobin levels.
- A C-section delivery is advised in the majority of cases of placenta previa. This is due to the fact that trying a vaginal birth when the placenta is covering or close to the cervix might result in severe bleeding, which can be fatal for both the mother and the infant. The timing of the C-section is determined by the circumstances and the gestational age of the baby.
- Contingent upon the level of the draining or different issues, the medical services proficient may choose to convey the child through C-segment early assuming it is considered significant for both the mother and the child’s government assistance.
- In the event that an unexpected labor is normal, the mother might be given steroid infusions to assist with speeding the child’s lung improvement, bringing down the opportunity of respiratory hardships in the infant.


Pingback: Placenta Accreta - Journey Of Mother
Pingback: Anterior Placenta - Journey Of Mother