Ovulation
What is Ovulation?
Ovulation is a normal process in the female reproductive system. The ovaries release a developed egg, which travels through the fallopian tubes and into the uterus for fertilization. Ovulation is a critical occurrence in a woman’s menstrual cycle since it is the optimal moment for conception to occur.
When does Ovulation Occur?
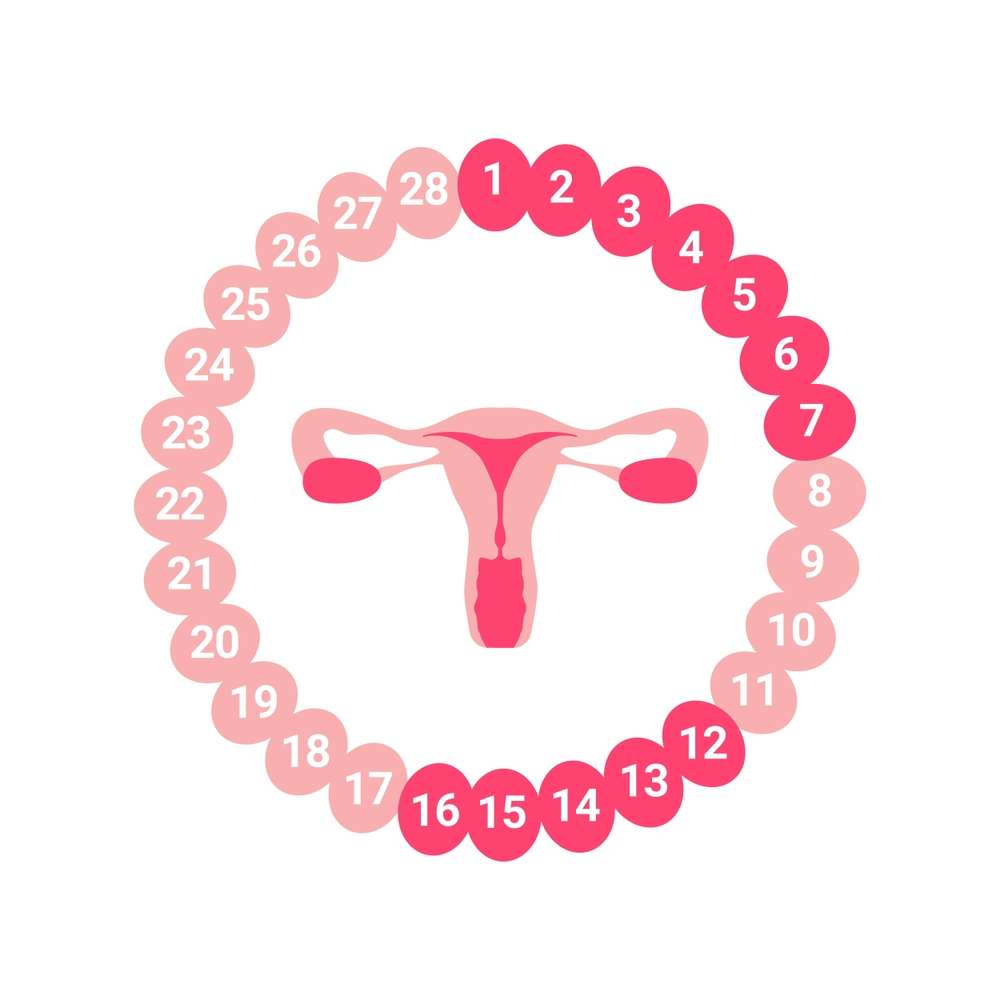
Ovulation usually happens towards the middle of a woman’s menstrual cycle. Ovulation normally occurs on day 14 of a 28-day cycle for women. It is crucial to note, however, that every woman is different, and cycle lengths might vary. To identify the precise timing, it is critical to understand your personal cycle and notice indicators of ovulation.
When is Ovulation?
Ovulation normally happens about two weeks before your next period. For instance, if you have a 28-day menstrual cycle, you will most likely ovulation around day 14. If your cycle is shorter or longer, the timing of ovulation will alter accordingly. Monitoring your menstrual cycle and looking for additional indications can help you determine the exact period of ovulation within your individual cycle.
How Many Days After Period is Ovulation?
The number of days following your menstruation that you ovulate can vary. Ovulation usually occurs around day 14 of a 28-day cycle, counting the first day of your menstrual period as day one. However, periods can last anywhere from 21 to 35 days, and ovulation occurs sooner.
How long does ovulation last?
The actual ovulation process usually lasts between 24 and 48 hours. The mature egg is discharged from the ovary during this time period and begins its journey to the uterus. The fertile window, which encompasses the days preceding and following ovulation, lasts for around six days. This is because sperm can survive in the reproductive canal for up to five days, boosting the odds of fertilization if intercourse occurs before ovulation.
How Many Days After Period is Ovulation?
The number of days following your menstruation that you ovulate can vary. Ovulation usually occurs around day 14 of a 28-day cycle, counting the first day of your menstrual period as day one. However, periods can range from 21 to 35 days, with ovulation occurring earlier or later as a result. It is crucial to note that menstrual cycles vary from person to person, and keeping track of your own cycle will help you pinpoint the days of ovulation.Pregnancy
How do I determine my ovulation day?
There are several methods for determining your ovulation day. Tracking your menstrual cycle is a common and convenient method. You can determine the approximate day of ovulation by keeping a note of the start and finish dates of your cycles. Monitoring cervical mucus changes, utilizing ovulation prediction kits, or tracking basal body temperature can also assist pinpoint the ovulation day more precisely. When these measures are combined and examined over multiple cycles, they can provide a more accurate picture of your personal fertility trends.
How to track ovulation?
Tracking ovulation is essential for couples attempting to conceive and can also be beneficial for those attempting to avoid pregnancy or better understand their monthly cycles. There are numerous methods for tracking ovulation:
- Menstrual Cycle Calendar: Use a menstruation calendar or a period tracking software to keep track of your periods. This entails keeping track of the start day of your cycle each month. Ovulation normally happens 14 days before your next menstruation. If you have a 28-day cycle, you may ovulate around day 14.
- Tracking your basal body temperature (BBT): Your basal body temperature is the temperature of your body at rest. After ovulation, it tends to rise somewhat (approximately 0.5 to 1 degree Fahrenheit). A specific thermometer specialized for tracking BBT is required. Take your temperature before getting out of bed every morning and record it on a chart. After ovulation, your temperature will rise.
- Changes in Cervical Mucus: Throughout your menstrual cycle, the consistency of your cervical mucus changes. It becomes transparent, slippery, and stretchy as ovulation approaches, comparable to egg whites. Sperm survival and motility are aided by this fertile cervical fluid. Take note of these changes and record them on a chart.
- Ovulation Predictor Kits (OPKs): These are available at most drugstores over-the-counter. The spike in luteinizing hormone (LH) that occurs 24 to 36 hours before ovulation is detected by OPKs. When the test line is as dark as or darker than the control line, it indicates that ovulation is imminent.
- Cervical Position: As you approach ovulation, your cervix changes position, becoming softer, higher, and more open. These changes can be tracked by gently feeling your cervix with clean hands. Take note of the variations in texture and position.
The Symptothermal Method combines many methods to improve accuracy. BBT and cervical mucus changes, for example, can be tracked together. - Ovulation applications: There are a plethora of smartphone applications available that can help you track your menstrual cycle, predict ovulation, and record other pertinent data such as mood, symptoms, and sexual activity. These apps frequently employ algorithms to calculate your fertile window.
- Fertility Monitors: Some of the most powerful fertility monitors integrate many tracking methods, such as BBT, cervical mucus, and LH tests, to provide a complete picture of your fertile window.
Ovulation cycle:
The ovulation cycle is the series of processes that take place within the female reproductive system that culminate in the release of an egg from the ovary. It is separated into three stages: the follicular phase, ovulation, and the luteal phase. The duration of the complete cycle varies across women, although it usually lasts between 21 and 35 days. Understanding your individual ovulation cycle might help you forecast when ovulation will occur and improve your chances of conceiving.
How long after your period does ovulation occur?
Ovulation occurs at different times for different women, although it usually happens about two weeks before the start of the next menstrual cycle. As a result, for women with a typical 28-day cycle, ovulation usually occurs around day 14. It is crucial to note, however, that menstrual cycles can vary in length, and hence the date of ovulation can also vary. Tracking menstrual cycles and observing physical signs such as cervical mucus can aid in determining the approximate period of ovulation.
How many days after ovulation does implantation occur?
Implantation usually occurs 6 to 12 days following ovulation, though this varies from woman to woman. Once fertilized, the egg travels down the fallopian tube and into the uterus. To develop a pregnancy, the fertilized egg, now known as a blastocyst, must attach itself to the uterine lining at this stage. Mild cramping and spotting are early indicators of implantation that some women may notice. It is important to note, however, that not all women experience visible implantation symptoms.
When can you test for pregnancy after ovulation?
It is typically suggested that a pregnancy test be taken at least 10 days after ovulation. This time frame allows the fertilized egg to attach into the uterine lining and the body to begin releasing pregnancy hormones. If you take a pregnancy test too soon, you may get a false negative because the levels of the pregnancy hormone, hCG, are not high enough to be identified. To avoid unnecessary misunderstanding or disappointment, it is best to remain patient and wait for an exact result.
What are the chances of getting pregnant during ovulation?
The likelihood of becoming pregnant during ovulation is relatively high. Ovulation is the best moment to get pregnant since it is when a developed egg is released from the ovary and ready to be fertilized by a sperm. Fertilization can occur up to 20-30% of the time in each menstrual cycle if the timing is perfect. However, it’s crucial to remember that a variety of factors, like overall health, age, and fertility status, can all influence these odds. A consultation with a healthcare expert might provide tailored insights regarding a person’s reproductive possibilities.
Ovulation symptoms:
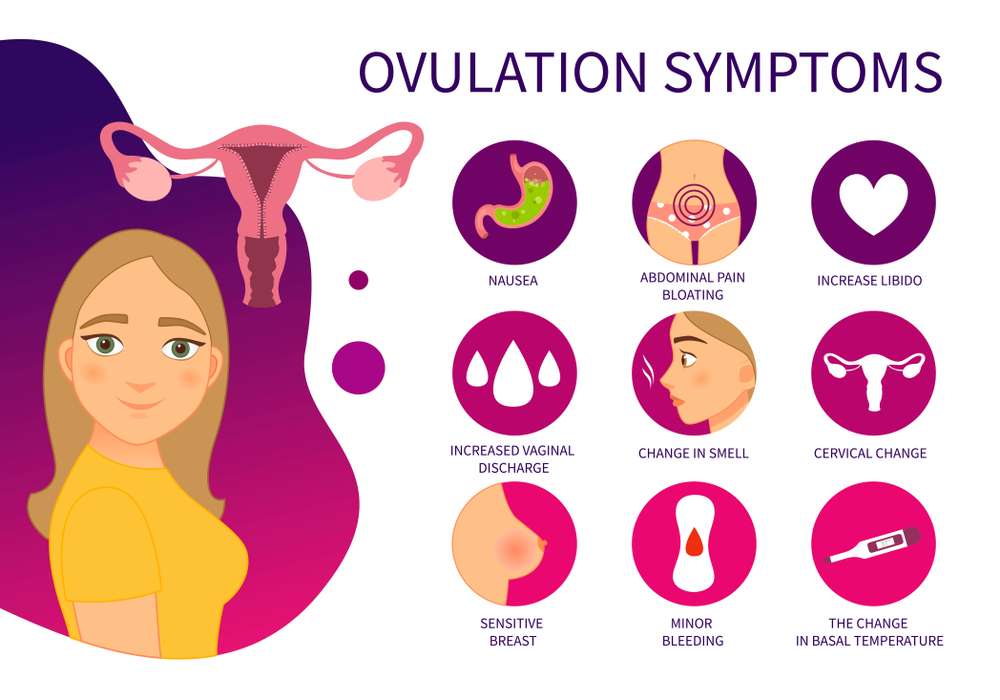
Ovulation can be indicated by a number of physical symptoms. Although not every woman may experience these symptoms, they can serve as useful markers. Common ovulation symptoms include:
Changes in cervical mucus:
The nature and volume of cervical mucus may alter as ovulation approaches. It frequently becomes transparent, slippery, and has the texture of egg whites.
Lower abdominal discomfort:
During ovulation, some women may have slight twinges or a dull aching on one side of their lower abdomen. The follicle rupturing to release the egg causes this discomfort, known as mittelschmerz.
Breast tenderness:
During ovulation, some women may experience breast tenderness or sensitivity, which is considered to be caused by hormonal imbalances.
Increased sexual desire:
Some people may experience an increase in libido around the time of ovulation. This increased sexual desire is related to the body’s innate impulse to reproduce.
modest rise in basal body temperature:
Using a specialized thermometer to track your basal body temperature during ovulation can reveal a modest spike in temperature.
Note:
Keep in mind that these symptoms might vary from person to person and that not all women experience them.
Ovulation bleeding:
Ovulation bleeding, also known as mid-cycle spotting, is light vaginal bleeding that occurs throughout the ovulatory period. It is usually distinct from a regular menstrual flow and appears as light pink or brown spots. While some women may have ovulation bleeding, it is not universal and is typically seen as a normal occurrence. If you have any concerns regarding unusual bleeding, you should talk with your healthcare professional.
Why am I experiencing bleeding during ovulation?
For some women, bleeding during ovulation, commonly known as ovulation bleeding, can be a baffling and frightening phenomenon. While not everyone experiences it, it is thought to be relatively common and generally harmless. Ovulation hemorrhage can occur when a tiny blood artery in the ovary ruptures as the egg is expelled. Typically, the bleeding is modest and appears as light pink or brown spots. However, if the bleeding is significant, protracted, or accompanied by extreme discomfort, it is best to visit a healthcare practitioner.
Is spotting during ovulation a good sign?
Spotting during ovulation might be a good indicator for many women. It often occurs when estrogen levels drop just before ovulation, resulting in the release of a little amount of blood. While it may be worrying for some, it is generally accepted as a fully normal and natural aspect of the ovulation process. However, if you have any concerns or if the spotting is accompanied by significant discomfort or other unusual symptoms, you should always talk with your healthcare professional.
Ovulation pain:
During ovulation, some women may suffer modest pelvic pain or discomfort. This is referred to as mittelschmerz, which means “middle pain” in German. It is distinguished by a painful or cramp-like sensation on one side of the abdomen, where the ovary is releasing the egg. While the pain is usually brief and goes away on its own, over-the-counter pain medicines can help if needed. If the pain is severe or chronic, it is best to seek medical attention.
Ovulation cramps:
Mild cramping or twinges on one side of the lower abdomen are frequent during ovulation and are known as ovulation cramps or mittelschmerz. These cramps are usually brief and vary in severity from woman to woman. They are normally regarded normal and are caused by the discharge of the egg from the ovary. However, if the cramps are severe or are accompanied by other troubling symptoms, it is best to seek medical attention.
Ovulation tracker:
An ovulation tracker, which is frequently available as smartphone apps or specialized websites, can be a useful tool for predicting and tracking ovulation. These trackers determine your fertile window, assist you in documenting symptoms and observations, and provide forecasts based on your cycle history. Keeping note of your menstrual cycle and accompanying symptoms can aid with family planning as well as provide insights into your general reproductive health.
Ovulation test:
An ovulation test, commonly known as an ovulation prediction kit (OPK), is a useful tool for establishing the fertile window and forecasting ovulation. It detects the presence of luteinizing hormone (LH) in your urine, which rises soon before ovulation. When the test shows a high LH level, it implies that ovulation is likely to occur within the following 24-48 hours. Ovulation tests can be a useful tool for women who are trying to conceive or want to better understand their menstrual cycle patterns.
Ovulation discharge:
The cervix produces fertile cervical mucus, also known as egg white cervical mucus (EWCM), during ovulation. This mucus is clear, elastic, and lubricating, with the consistency of raw egg white. It plays a crucial role in facilitating sperm passage through the reproductive canal and promoting conception. Observing variations in cervical mucus might provide you crucial information about your fertile days and help you identify ovulation.
What are the signs of ovulation discharge?
Ovulation discharge, often known as cervical mucus, is a good predictor of conception. As a woman approaches ovulation, her body produces more estrogen, causing cervical mucus to thin, clarify, and become more slippery. This change in consistency aids sperm movement through the cervix and into the fallopian tubes, boosting the likelihood of conception. Women can determine their most fertile days and improve their chances of conception by monitoring changes in cervical mucus.
What does ovulation discharge look like?
Ovulation discharge might differ from one woman to the next, but it usually has different characteristics. Cervical mucus becomes transparent, slick, and stretchy during ovulation, comparable to raw egg whites. This consistency shift is intended to improve sperm survivability and mobility, allowing them to move more easily through the reproductive system. Observing this type of discharge can be a helpful predictor of fertility and the best time to conceive. It’s vital to remember that women’s cervical mucus might vary, so it’s critical to pay attention to one’s own trends over time.
Why do some women experience brown discharge during ovulation?
Brown discharge during ovulation can be caused by a variety of circumstances. It is frequently seen as a harmless consequence of the ovary’s egg discharge. When blood becomes older and takes longer to exit the body, the hue changes to a darker tone. Furthermore, hormonal shifts that occur during ovulation can contribute to this condition. While these symptoms are normally not cause for concern, it is always a good idea to talk with a healthcare physician if they persist or are uncommon.
Can you get pregnant after ovulation is over?
While the window of fertility is often centered on ovulation, it is still possible to become pregnant after ovulation. Sperm can live inside the female reproductive system for up to five days, so if intercourse occurs a few days before ovulation, fertilization is still possible. However, as time passes after ovulations, the probability reduces substantially, making the immediate pre-ovulation period the most fertile.
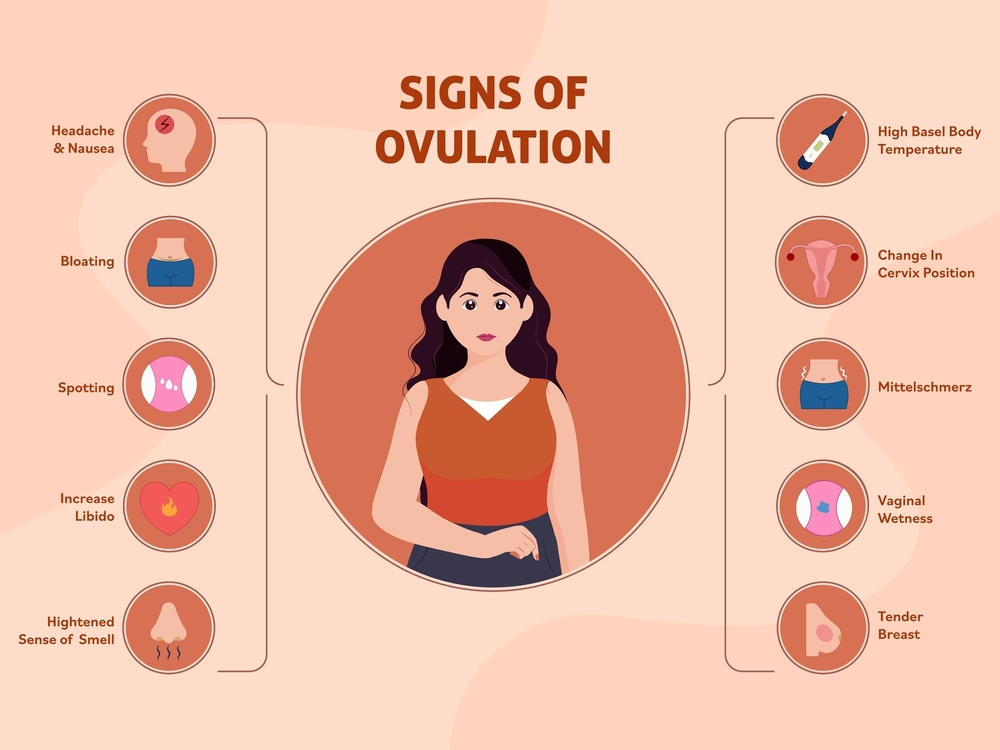
Signs of Ovulation:
In addition to the physical symptoms stated previously, there are other signals that ovulation is occurring. These are some examples:
- Ovulation test results that are positive: An increase in luteinizing hormone found by an ovulation test is a strong indicator that ovulation is about to occur.
- Changes in cervix position: During the menstrual cycle, the cervix undergoes changes in position and hardness. As ovulation approaches, the cervix softens, rises, and widens to allow sperm to enter.
- Hormonal changes during ovulation might cause an increase in sexual desire.
- As previously stated, some women experience slight pain or twinges during ovulations.
- Breast tenderness: During ovulations, hormonal variations might cause breast sensitivity or pain.
- It’s crucial to realize that these indications aren’t perfect, and combining them can provide a more accurate picture of ovulation.
Does Plan B Work During Ovulation?
Plan B, popularly known as the “morning-after pill,” is an emergency contraception method intended to lower the risk of pregnancy following unprotected sexual contact or contraceptive failure. Plan B works by delaying or suppressing ovulation, preventing the release of a fertilized egg. However, if ovulation has already occurred, its effectiveness is greatly reduced. To maximize its efficiency, Plan B should be taken as soon as possible after unprotected sex.
Can You Get Pregnant After Ovulation?
While the chances of becoming pregnant after ovulation diminish, it is still possible to conceive within a certain interval. The egg survives for about 12 to 24 hours after it is discharged from the ovary. Because sperm can survive in the female reproductive system for up to five days, the viable window extends a few days before and beyond ovulation. As a result, if intercourse happens at this time, fertilization and pregnancy are still possible. It is critical to note that the egg must be fertilized within this limited time frame in order to result in pregnancy.
What are the chances of getting pregnant during ovulation using the pull-out method?
The withdrawal method, commonly known as pull-out, is not regarded a viable type of contraception, especially during ovulation. While it is true that ejaculation outside the vagina reduces the chances of conception, there is still a possibility of pregnancy. Pre-ejaculatory fluid can include sperm, and it only takes one sperm to fertilize an egg. As a result, relying only on the pull-out approach during ovulation is not advised. To avoid unintended pregnancies, it is critical to investigate more effective and dependable contraceptive solutions.