Tubal pregnancy
Introduction:
A tubal pregnancy, also known as an ectopic pregnancy, is an uncommon but deadly pregnancy disease that can develop in women. In this post, we will look at tubal pregnancy, including what it is, what causes it, and what therapies are available.
What is tubal pregnancy?
A tubal pregnancy occurs when a fertilized egg implants outside of the uterus, generally within the fallopian tube. Unfortunately, the fallopian tube is not meant to support embryo growth, which can result in a variety of problems and sometimes life-threatening conditions if addressed.
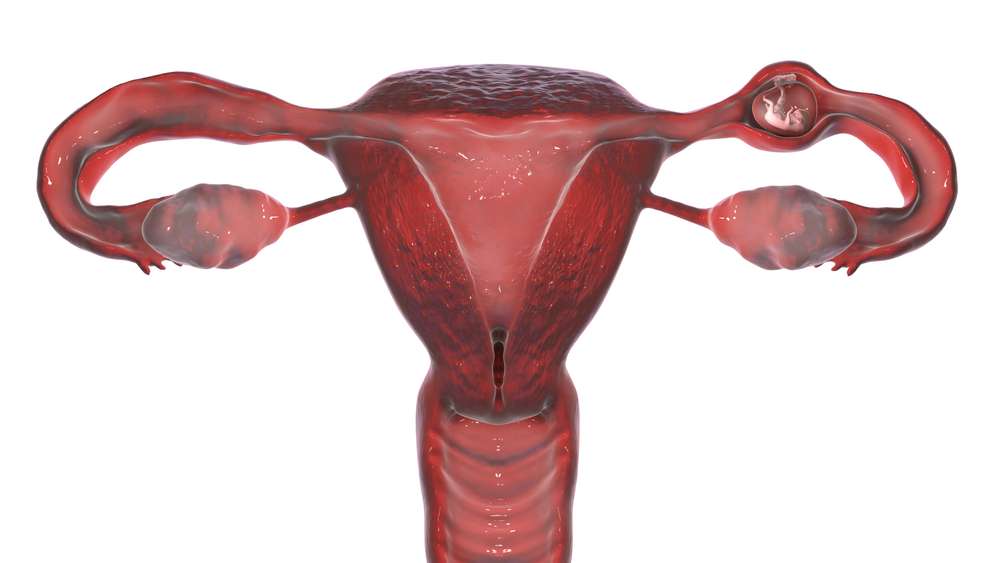
What does a Tubal Pregnancy Feel Like?
A tubal is frequently described by women as a persistent, severe ache in the abdomen or pelvic. Some people may also have vaginal bleeding, shoulder pain, or dizziness. The severity of these symptoms can vary and may worsen over time.
Where is Tubal Pregnancy Pain?
Pain from tubal is usually felt on one side of the abdomen or pelvic. This is due to the fertilized egg implanting and growing within the fallopian tube, causing stretching and discomfort in the afflicted location.
What Causes a Tubal Pregnancy?
The most common reason of a tubal is a broken or clogged fallopian tube, which prevents the egg from moving towards the uterus. This can happen owing to a variety of circumstances, including:
- PID (pelvic inflammatory disease)
- Tubal or pelvic surgery in the past
- Endometriosis
- Unbalanced hormones
- Anomalies of the fallopian tubes that occur at birth
Tubal pregnancy symptoms:
Aside from stomach pain, tubal can cause the following symptoms:
- Vaginal bleeding that can be lighter or heavier than a normal menstrual period
- Vomiting and nausea
- Weakness and exhaustion
- Lightheadedness or faintness
Abdominal pain:
Sharp, stabbing pain in the lower abdomen or pelvis, usually on one side, is the most prevalent symptom. The pain may be intermittent or continuous.
Spotting or vaginal bleeding:
Some women suffer spotting or vaginal bleeding, which can be confused with a normal menstruation or implantation bleeding.
Shoulder discomfort:
In certain situations, discomfort from a tubal pregnancy may radiate up to the shoulder area, usually owing to diaphragm irritation from blood or fluid.
Nausea and Vomiting:
Because of the pain and hormonal changes connected with pregnancy, you may feel queasy or vomit.
Internal bleeding from a ruptured ectopic pregnancy can induce a reduction in blood pressure, resulting in dizziness or fainting.
Weakness and Fatigue:
You may feel weak and exhausted as the ectopic pregnancy advances and produces bleeding.
urine or bowel alterations that are frequent or uncomfortable: Some women report changes in their urine or bowel habits, such as increased frequency or discomfort.
Note:
It’s crucial to note that not all women who have a tubal pregnancy will have all of these symptoms, and others will only have a few. Furthermore, the severity of the symptoms can vary. If you suspect a tubal pregnancy or are suffering significant stomach pain and bleeding during early pregnancy, get medical assistance immediately. An ectopic pregnancy is a medical emergency, and prompt identification and treatment are required to avoid complications such as a ruptured fallopian tube, which can be fatal.

Signs of tubal pregnancy:
Recognizing the indicators of a tubal pregnancy early on is critical, as immediate medical intervention can considerably lessen the risks. Some warning indications include:
- Vaginal spotting or abnormal bleeding
- One side of the abdomen is experiencing pain.
- Difficulty distinguishing between a tubal pregnancy and a normal pregnancy with a home pregnancy test
How Do You Know if You Have a Tubal Pregnancy?
If you feel you have a tubal, you should seek medical assistance right once. Several tests may be performed by healthcare experts to confirm the diagnosis, including:
- A pelvic examination is performed to assess discomfort and tenderness in the pelvic region.
- Pregnancy hormone levels are measured via blood testing.
- Ultrasound imaging is used to find the implanted embryo outside of the uterus.
Tubal pregnancy treatment:
The treatment option for a tubal pregnancy may be determined by a number of criteria, including the pregnancy’s viability, the woman’s overall health, and her future reproductive objectives. Treatment options include non-surgical therapies as well as surgical procedures that may include:
- Medications to halt embryo growth and cause resorption by the body
- Laparoscopic surgery is used to remove the ectopic pregnancy while leaving the fallopian tube intact.
- In severe circumstances, if the tubal has ruptured or poses a major risk, the fallopian tube may need to be removed totally.
Tubal pregnancy surgery:
To treat a tubal pregnancy, there are two basic surgical approaches:
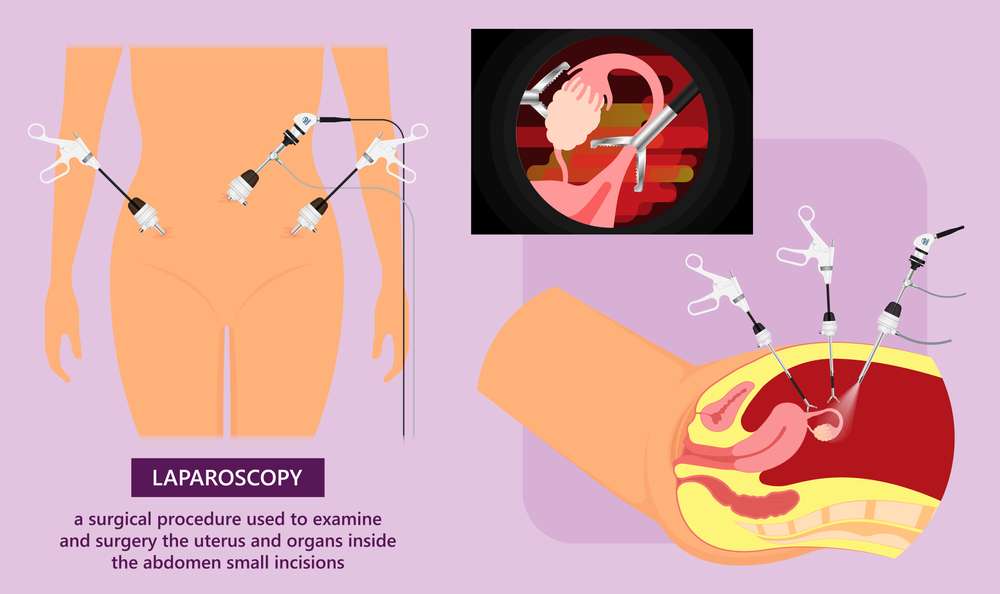
Laparoscopic Surgery:
Laparoscopic surgery is the most commonly used and least intrusive method of treating ectopic pregnancies.
To visualize the pelvic organs, the surgeon makes a small incision at the navel and inserts a thin, flexible tube with a camera (laparoscope) into the belly.The surgeon may execute one of two operations, depending on the severity and location of the ectopic pregnancy:
- Salpingostomy: A small incision is made in the afflicted fallopian tube and the ectopic pregnancy is removed while the tube is preserved.
- Salpingectomy: If the fallopian tube is significantly damaged or burst, the surgeon may need to remove the afflicted tube totally to prevent potentially fatal bleeding.
Open Abdominal Surgery:
Open abdominal surgery may be required in more complex cases or when laparoscopic surgery is not possible.A wider incision in the lower abdomen is made to directly access and remove the ectopic pregnancy or the damaged fallopian tube. Open surgery is often reserved for instances in which laparoscopic surgery is not possible or when difficulties arise. The surgical technique used is determined by a number of factors, including the woman’s overall health, the location and state of the ectopic pregnancy, and the surgeon’s experience.
Note:
Following surgery, the patient must follow post-operative care recommendations, which include monitoring for any signs of infection or problems, taking any prescribed medications, and attending follow-up appointments with their healthcare practitioner.
If you suspect you have an ectopic pregnancy or are experiencing symptoms such as abdominal discomfort, vaginal bleeding, dizziness, or shoulder pain, get emergency medical assistance. Early detection and action are critical to achieving the best potential result.
What Are Your Chances of Getting Pregnant After Tubal Ligation?
Tubal ligation is a permanent sterilization surgery in which the fallopian tubes are blocked or sealed. While it is highly efficient in preventing pregnancy, there is still a small possibility of pregnancy following the surgery. The chance of tubal after tubal ligation is low but not non-existent.
Conclusion:
A tubal is a serious medical condition that necessitates prompt medical treatment and management. Recognizing the symptoms, understanding the causes, and getting treatment as soon as possible will assist to reduce the potential hazards connected with this illness and protect the health and well-being of afflicted women.


Pingback: Ectopic Pregnancy - Journey Of Mother